FIELD & FUNDUS
DR. REZAUL MURSHED
M.B.B.S(DMC)D.O(D.U)
AHMAD MEDICAL CENTER
DHAKA BANGLADESH
Fax: 00-88-02-8117364
E-mail: amc@bol-online.com
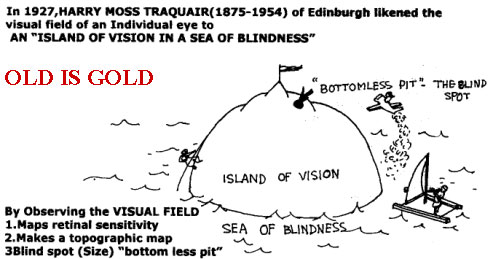
HISTORY
Key Issue
Understanding the PrinciplesHUMPHREY IS GOLD STANDARD
GOOD THINGS ARE CHEAP BUT CHEAP THINGS ARE NOT GOOD

STATIC vs KINETIC
STATIC
- Quantitative
- VFD detected earlier than kinetic, with 20% nerve damage
- Area is fixed but Stimulus varies in intensity
- Three dimensional
- Computerized
- Threshold type
- Less Error
- Quality & Expensive
- Good both for Glaucoma & Neurological
KINETIC
- Qualitative YES/NO
- VFD when 40% nerve damage
- Fixed stimulus seen from seeing to non seeing, area is not fixed.
- Two dimensional
- Not Computerized
- Non Threshold
- Man behind Perimeter
- Not used so much
- Good for Neurological
WHAT IS PERIMETRY
Is the measurement of the differential light Sensitivity of the retina at a defined number ofLocations.
HOW TO INTERPRET THE HUMPHREY FIELD FOR GLAUCOMA & NEUROLOGICAL CASES
WHEN WILL YOU SEND A PATIENT FOR FIELD?
SUSPECTED OR ESTABLISHED GLAUCOMA
- OPTIC NERVE HEAD CHANGE OR NERVE FIBER LAYER DEFECT
- VISUAL FIELD DEFECT
- RAISED INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE
WHEN ONE OF THE THREE IS SEEN THENGLAUCOMA IS SUSPECTED.
WHEN ANY OF THE TWO ARE SEEN THEN GLAUCOMA IS ESTABLISHED.
GLAUCOMA SUSPECT BY THE EUROPEAN GLAUCOMA SOCIETY
OCULAR HYPER TENSION
AAO Vol. 109,Number 3,March 2002

NORMAL GROUP
AAO VOLUME 109,NUMBER 3,MARCH 2002
The Eye Care America Glaucoma Project
Is your patient or their family at Risk forGlaucoma? Score below to see.
| 1.Family History (Chose one) | No F/H | 0 |
| Parent & Child has glaucoma | 2 |
|
| Siblings | 4 |
|
| Parents & Siblings | 4 |
|
| 2.Race(Chose one) | Caucasian | 0 |
| Hispanic | 1 |
|
| Black | 3 |
|
| 3.Age(Chose one) | <40 | 0 |
| 39-49 | 1 |
|
| 49-59 | 2 |
|
| 59+ | 4 |
To Score: Add one score in each of the above categories. If you have atotal score 4 or higher, you have a high risk for having Glaucoma.
GREATER RISK OF GLAUCOMA
Risk Factors
Now CCT
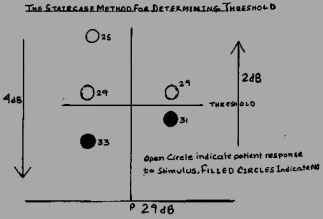
THRESHOLD
THRESHOLD IS THE CRUCIAL CONCEPT IN PERIMETRY
Threshold is the dimmest stimulus seen by the a subject,50% of thetime. Measured in decibels(dB) in automated perimetry. Higher thedB minimum is the light, lower the dB (0dB) brightest is the light.
0dB=Brightest light
40dB=Dimmest light
The Threshold of Sensitivity
The threshold is the crucial concept in perimetry. The threshold is the dimmestLight seen by a subject, 50% of the time.
NORMAL THRESHOLD VALUES
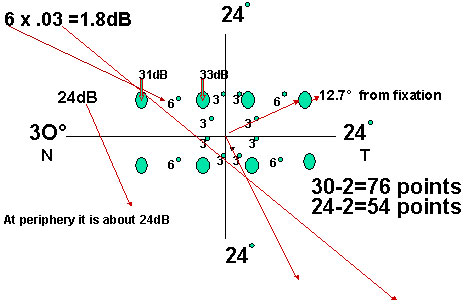
First four paracentral points are 3 ºfrom vertical & horizontal lines,12.7 º from the fixation point & next all stimulus points are 6 degree apart.
Maximum threshold is at the fovea say,35dB dimmest light,with each degree to periphery threshold decreases by .03 dB.
STRATEGY/METHOD/TECHNIQUE HUMPHREY HAS MANY OPTIONS
| FULL THRESHOLD | 1983 |
Normal 12-20 Min |
| FASTPAC | 1991 |
Normal 10-15 Min |
| SITA | 1997 |
SITA STANDARD= FULL THRESHOLD Normal 5-8 Min
SITA FAST= FASTPAC Normal 3-5 Min
STRATEGIES ARE
| FULL THRESHOLD | 1983 |
20-30 Min |
| FASTPAC |
1991 |
14-20 Min |
| SITA | 1997 |
Swedish InteractiveThreshold Algorithm5-8 Min

SITA
SITA STANDARD 24-2
SO USING FASTER STRATEGIES
Reduce the fatigue effect caused by both
- Retinal fatigue
- Physical fatigue
Therefore a quicker test can be morereliable and accurate compare to testing with longer elaborate test strategies.
Types of Glaucomatous field loss
Aulhorn's & Harms' classification of glaucomatous field loss
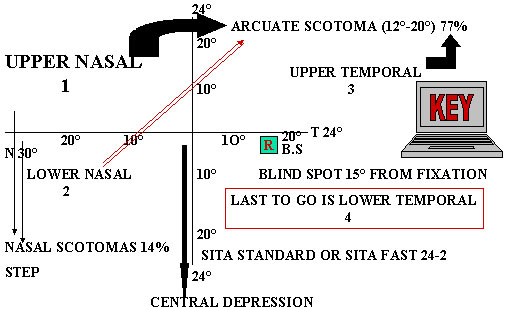
THE KEY PATTERN DEVIATION PLOT CHART
Scotomas are seen in the Suspected & Expected zones
LOOK ONLY LOWER RIGHT DEVIATION PLOT CHART
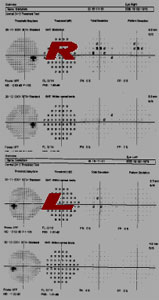
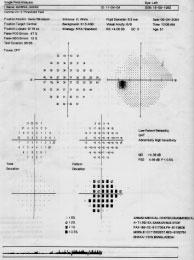
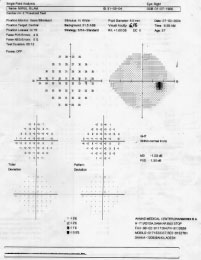
SINGLE FIELD ANALYSIS
SINGLE FIELD ANALYSIS
-
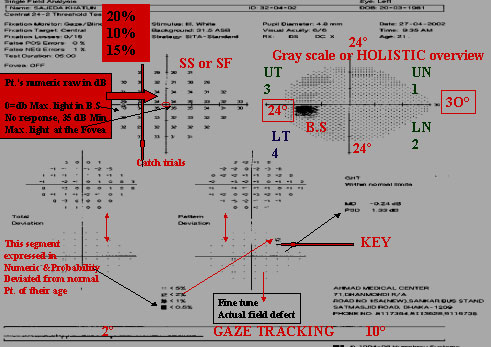
Name,ID ,DOB,R/L, pupil size& age. Next is SIX IN ONE
-
Upper left Parameters, Stimulus size, back ground 31.5 dB, Catch trialPupil dia, V.A. Near Correction, Date, Time, Age
-
Upper right GRAY SCALE
-
Upper left next to Gray scale is NUMERIC DATA, thisis the raw data printed in numbers that express the patient's response in dB.
-
A. This segment is expressed numerically and probabilityPlots (5B) of abnormality demonstrates how the patient'sresponses deviated from known normal patients of theirage. Middle left (5A) aged matched Numeric data.lower left aged matched probability plot (5B)
-
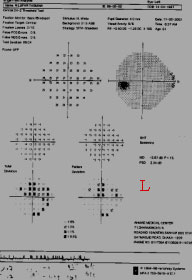
A.PATTERN DEVIATION : This is the KEY PLOT.The pattern deviation fine tune and enhance the totaldeviation data. It corrects total deviation from any mediaopacity (cataract), miotic pupil. It also displayed as botha numeric (6A) difference and with probability analysisPlots(6B).Any real localized defect is seen in this plot.Middle right Numeric data & Lower right( 6B ) probabilityPlot chart (Actual picture of the patient)
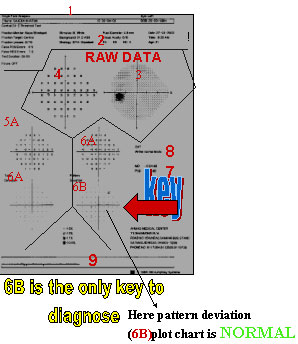
EVALUTING OF A SINGLE FIEL
2. Reliability indices
3 &4. Raw data and gray scale
5. A & B Total deviation
6. A & B Pattern deviation
7. Global Indices (MD & PSD)
8. Glaucoma Hemifield test (GHT)
9. Gaze Tracking
If you can correlatethe disc with PatternDeviation ProbabilityPlotTHAT'S ALL.
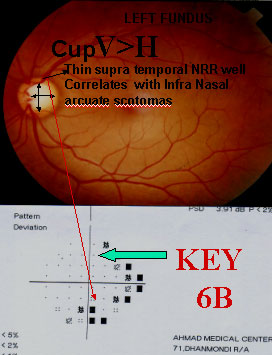
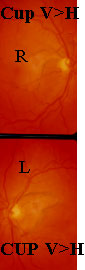
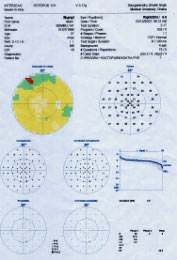
HERECUP V>H Thin supNRR gives inf. arcuateScotoms which laterjoins the inf nasal step.Here superior nasalstep is also seen. Anestablished case ofearly POAG. She hadstrong F/H & raisedIOP.
KEY POINTS
PATTERN DEVIATION PLOT CHART
IF YOU CAN ONLY READ THE PATTERN DEVIATION PROBABILITY PLOT CHART 6B THATS ALL.
OF COURSE IT MUST CORRELATES WITH THE DISC

Time : If it exceeds its normal then it'slikely to be a Path. VFSS 5-8 Min SF 3-5 Min
UPPER LEFT
Fixation Monitor/Gaze Blind Spot: On the upperleft side of the printout. Patient's eye ismonitored by fixing the eye towards a yellowlight. At the beginning of the test after fixation5% of the supra threshold a type of stimulusis given on the B.S. to find out central fixation.This is called HEIJL-KRAKOW method. Herefixation target is central. If there is any macularpathology instead of central fixation we choosesmall diamond or large diamond just below thecentral fixation. (See Slide 31).
FL is a tricky thing. It should be within 20%,but itwill be a reliable VF with high FL, but low FP & FN.
FP TRIGGER HAPPY it should be below 10%.Itmeans that the pt. pressed the switch without seeing thelight.
FN First a low intensity light is seen. At the same pointa brighter stimulation (more than 9dB) is given to see ifPt. is alert or not. Its normal value is 15%but in Path.Condition it goes up above normal level.
INSIDE HUMPHREY PERIMETER
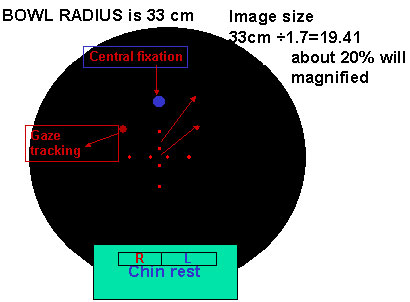
A lesion in the retina is twenty times magnified in the bowlOptic nerve is 1.5mmx20=30mm which seen in reduced form.
RELIABILITY PARAMETERS
| UPPER LEFT SIDE |
Normal |
| FIXATION LOSS |
20% |
| FALSE POITIVE |
10% |
| FALSE NEGATIVE |
15% |
FOVEAL THRESH HOLD
20 yrs. 35 dB
30 yrs. 34 dB
70 yrs. 30 dB
FT decrease 1 dB per 10 yrs.
If FT measures above 30 dBV.A. will be above 6/12
0 dB=Brightest light in moonLit night40 dB= dimmest light
|
Octopus Decibels HUMPHREY |
|
40 |
50 |
30 |
40 |
0 |
10 |
FP=It is better to omit than to commit
UPPER RIGHT GRAY SCALE
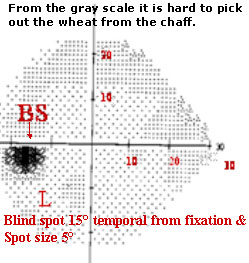
This is a "HOLISTIC" overview on the displays the patient's responses in various shades of grey instead of printing numeric data. It is of little clinical value. In octopus it is colored. From gray scale it is hard to pick out THE WHEAT from Chaff.
SEARCHING FOR A
NEEDLE IN HAY
STACK
A GLANCE GUESS FROM GRAY SCALE
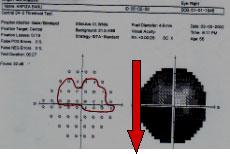
This 56 yrs. middle aged lady whose rt. eye vision is 6/9 FT 32 dB. Only a small nasal NRR persists which represents a small central vision with a small temporal island of vision remains, all other parameters are excellent.

ONLY GROSS DEFECT
This young lady of 23 is an established case of RP. Her both discs are palewith jet black spots in the peripheral retina, parents were cousins, sister andbrother, H/O night blindness,V.A.6/6 with very good FT 37 dB,D/D 1.R.P 2.lens rim defect 3.Retinoschisis 4.Pan retinal photo coag5Peripheral retinal degeneration 6C.R.O ..7.Aphakic glass.
GRAY SCALE
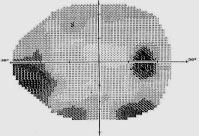
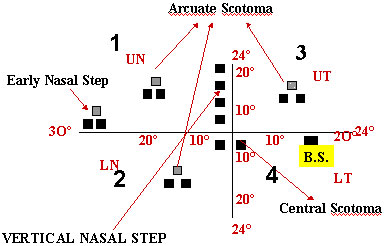
Early Nasal Stap
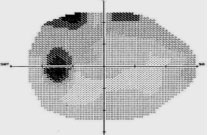
Deformed Disc
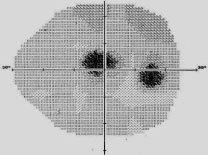
Paracentral Scotoma

Typical Sup Arcuate Scotoma From B.S to Join Sup Nasal Step
TYPES OF SCOTOMAS
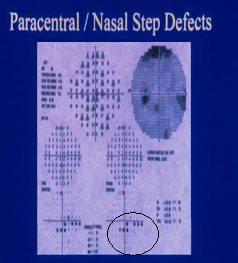
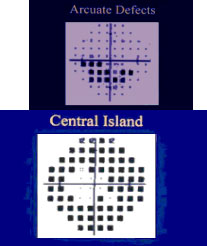
CREENING TEST
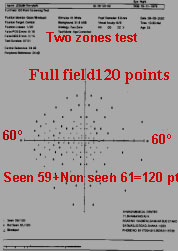

A screening test of the same RP case. Two zones with central and peripheral ref. were 34dB.Outof 120 points pt. sees only 59 points R/E & 40 points in L/E.It's a suprathreshold type of test.A threshold test should be performed when a pt. cannot see 10 points out of 120 points or atany area 2 or 3 adjacent points of non seen points are detected.
SCREENING PROGRAMS HFA II
|
TEST PROG
|
AREA & POINTS
|
APPLICATION
|
|
CENTRAL 76
|
30 °
|
GLAUCOMA
|
|
76 Points
|
Neurological
|
|
|
Full Field 120
|
60 º
|
General
|
|
120 Points
|
Glaucoma
|
|
|
Neurological
|
SCREENING FOR GLAUCOMA MAJOR POINTS
NAME DOB ID

V.A 6/6 B/E
IOP Normal
C;D
Rt. .4
Lt. .6
Plan
Repeat VF

By mistake her DOB was given 1969, instead of 1959.Gray scale shows slightDeep GHT GRS. But when her exact DOB is given 1959,GHT is WNL. So,always give Correct DOB as well as last corrected distance vision.
BUT THIS IS A HIGHLY SUSPECTED FIELD.
PUPIL SIZE 3 TO 7 mm

One EYED
established
POAG ON
AntiGlaucomaDrug

All fields should be done with normal reacting pupil within 3-7 mm in size. Dilated pupilgives less false result than the small pupil. So, please check pupil size before seeing a Visual field (VF) Humprey's latest version 12.3 will give you the pupil size on the screen before starting the field.
PUPIL SIZE
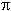 x r2
x r2
GHT & PROBABILITY
<5% = Significant
<0.5% = More Sig.
IN THELOWER
MIDDLE

GHT- This test assumes that glaucoma does not cause a generalized Global depression of the field of vision. It takes advantage of the asymmetric field loss pattern generally seen in glaucoma. The testanalyses defects in the superior hemi field and makes comparisonwith mirror image locations in the inferior hemi field.
- GHT may be OUT SIDE NORMAL LIMIT (ONL)
- BORDER LINE (BL)
- GENERAL REDUCTION OF SENSITIVITY (GRS)
- ABNORMALLY HIGH SENSITIVITY
- WITH IN NORMAL LIMIT (w.N.L)
GHT
The GHT has been evaluated by both Peter Åsman and Heijl(1992) and by Katz(1996). IT WILL GIVE YOU FIVE RESULTS.
- Abnormally high sensitivity. The general height of the field is beyond the 99.5% limit for normal.
- Out side normal limits (ONL) - The asymmetry is beyond the 99% limit for normal in any of sector pairs. If seen twice in two consecutive fields early glaucomatous defect criteria by "Anderson".
- Borderline (BL) - The asymmetry is beyond the 97% limit for normal in sector pairs. It's not a pathological field.
- General reduction in sensitivity (GRS) - The general height is below the 0.5% limit for normal. Seen in Cataract, High Myopia, Media opacity, Dilated pupil.
- Within normal limits (WNL) - When none of the above four criteria are seen.
GAZE TRACKER
By seeing this tracing at lower end of the field you can judge whether the fixation is OK or not.


AT THE BOTTOM OF THE FIELD
SEEN JUST BELOW THE GRAY SCALE
GLOBAL INDICES MD (Mean deviation) Or mean defect- The mean deviation is theaverage difference between the patient'soverall sensitivity and that of age matchedcontrols. High MD seen in case of Normal:
- Cataract
- Miosis
- Ref.error
- Fatigue
Then PSD will be normal.
PSD: Is an index of unevenness in amountof field calculated from Pattern deviationPlot chart. (Normal up to 2.5)
INTERPRETATION CRITERIA INTERPRETATION CRITERIA
AN EARLY FIELD DEFECT ACCORDING TO "ANDERSON "
Cluster of 3 or more adjacent points in an expected, suspected location (Typical for glaucoma) of central 24 degree field. ON AT LEAST
OR
Glaucoma Hemi field test (GHT) Outside normal for at least two consecutive Fields
OR
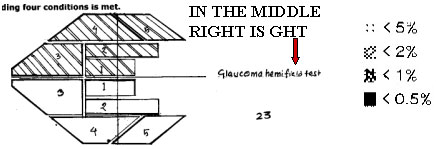
Cycling can't be learned in a day

LEARNING CURVE
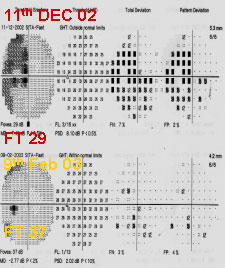
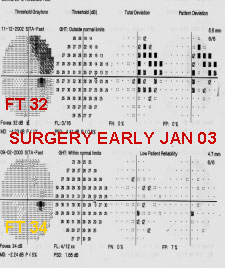
First field is not always areliable field (of course notall the time). She is a youngschool teacher. First VF done after seeing her IOP R30 &17 L. healthy NRR .6 & .5 are the cup : disc ratio R/L respectively. Since 5 th June '00 she was on anti- Glaucoma drug. We stopped her drops after Seeing the 2 nd field .On the3 rd field on 29 th Oct '01 herVF is within Normal limit & IOP too. It's a long term fluctuation.
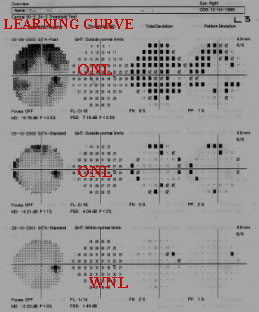
FOLLOW UP
PATIENT IS WITH BETA BLOCKER DROP SCINCE SEPTEMBER 2001
First field is not always reliable

Field done out side BANGLADESH

This young girl of 10 yrs.has been dig. in Marfan Sy with NTG.It can not occur before 45yrs.Diag.Out side BD.In Dhaka It has been dig. Marfan Without Glaucoma her first field is not reliable. Second field done at Dhaka is OK GHT ONL is due to high myopic cylinder.Doing field is like a Baby sitter. Glaucomamay be associated with sub laxation of the lens.Here her IOP is normal Her both NRR are healthy.
I LOVE MY COUNTRY
BEFORE SENDING THE PATIENT
- GIVE LAST CORRECTED DISTANCE VISION
- DETAIL OF OPTIC NERVE EXAMINATION IF POSSIBLE WITH DIAGRAM
- INTRA OCULAR PRESSURE (IOP)FLEXIBILITY IS THE ENEMY OF STANDARDIZATION
Field done out side BANGLADESH
A LABORIOUS THRESHOLD TEST HIGH RESOLUTION PATTERN MAY FERRET OUT EARLY SIGNS OF GLAUCOMA.BUT IT MAY ALSO GENERATE ARTIFACTS, IF THE PATIENT'S ENDURANCE IS STRESSED BEYOND 20 MINUTES PER EYE "LEADERSHIP IS LIKE SWIMMING CANNOT BE LEARNED IN A "DAY" OFTEN TO GET A RELIABLE FIELD YOU HAVE TO DO ONE FIELD EACH MONTH FOR THREE CONSECUTIVE MONTHS OF COURSE NOT ALL THE TIME.
PLEASE TELL YOUR PATIENT THAT IT ISA TIME CONSUMING TEST.TELL HIM OR HER TO TRY TO COME IN THE MORNING. IT'S A PSYCO PHYSICAL TEST.TELL THEM NOT TO BE IN HURRY.HE OR SHE MAY MISS THE BUS, WITH AN UNRELIABLE FIELD.

COMMON PROBLEMS WITH PERIMETRY
REPORT

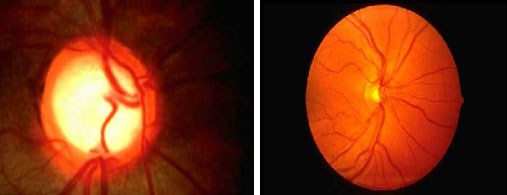
PHYSIOLOGICAL FUNDUS
She is a young lady of 27yrs.old. Her IOP are normal. But big C;D .65 B/E, her Doctor put her anti Glaucoma drop.But her fundus NRR is healthy& ISNT rule is ok. Her two consecutive fields are normal as well her B/Y field are O.KIt's a normal PHYSIOLOGICAL DISC


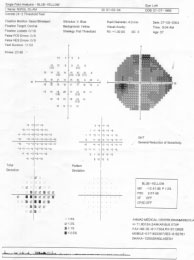
BACK
GROUNDIS YELLOW& THE VIS THE BLUESTIMULUSSIZE

- HIGH INTER-INDIVIDUAL VARIABILITY
- LENS ABSORPTION
- PATIENT FATIGUE
- LONG ADAPTION TIME
- UNPLEASANT
- ONLY PATIENT UNDER 40YEARS !?
BACKS B/Y
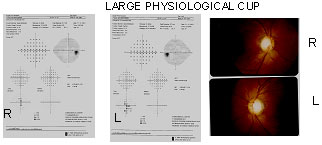
This young man of 34yrs a typist came for red eyes. V.A. 6/6 B/E and IOP !7 mmhg. Both Funds showed ISNT rule are OK.Fields are normal too. It's nothing but a normal physiological cup.still than he should be on follow up.
ALWAYS CORRELATES WITH THE FUNDUS
GLAUCOMA
NORMAL TENSION GLAUCOMA
A CONDITION IN WHICH GLAUCOMATOUS CUPPING OF OPTIC NERVE HEAD, LOSS OF NERVE FIBER LAYER AND VISUAL FIELD LOSS OCCURS AT AN IOP BELOW <21mmHg MEASURED AT DIFFERENT TIMES, WITH OPEN AND NORMAL APPEARING ANGLE .
VARIENTS OF NTG
OPTIC NERVE HEAD CHANGES IN NTG
VISUAL FIELD DEFECT
OTHER ASSOCIATES OF NTG
Differential Diagnosis of NTG
DIAGNOSIS of NTG
OCULAR EVALUTION :
Apart from routine ocular & FUNDUS examination.
LOOK FOR
- Central corneal thickness(520 µM) , thin cornea may give false low IOP reading,POAG might appear as NTG
- Record of a diurnal curve
- Perimetry
- HRT
- Record of ocular blood flow
MEDICAL EVALUTION
- Cardiovascular examination including 24 hrs. BP monitoring to rule out nocturnal hypotension, Carotid artery Doppler imaging to assess blood flow, capillary filling time on exposure to cold.
- Complete blood picture, ESR, Blood profile, Lipid profile to ruled out Hypercholesterolemia
- MRI to ruled out Diffuse cerebral ischemia
MANAGEMENT OF NTG
Goal of treatment is to preserve the visualFUNCTION
Non-Progressive form does not require anytreatment, as it rarely progresses. Monitoring& follow up is required every 6-12 months.
Progressive form needs treatment. Targetshould be to reduce 30% IOP from the initial, maydelay the progression.
NTG
TREATMENT
PROGRESSION OF NTG
PLAN OF TREATING LTG
-
VERY DIFFICULT TO TREAT AS WELL AS TO DIAGNOSE
-
FIRSTLY, TO REDUCE THE IOP BY 30%. HER IOP WAS 15WE REDUCED HER IOP TO 15X.7=10.5MmmHg WITH AZOPT
-
IF HER IOP BECOMES BELOW 10 THERE IS NO NEED OF DOING Visual Field
-
THINK BEFORE USING BETA BLOCKER DROPS IN NTG
-
PHASING TO BE DONE
-
If medical treatment fails then ALT has to be tried, if it also fails go for Surgery
-
24 Hrs. MONITORING OF B.P. IF DIAS DIPS DOWN AT NIGHT BELOW 60 mmHG AND PT IS HYPERTENTSIVE AND IF HE/SHE IS ON BETA BLOCKER TYPE OF DRUGS THEN THAT SHOULD BE CHANGED.CONSULT WITH CARDIOLOGIST IOP/BP
-
Neuro protector Vit E. Aspirin, aerobic exercise, anti oxidant can be used to improve perfusion. TRY TO CORRECT HYPOTENSION.
-
What to do when there is High BP with Glaucoma? TOUGH QUESTION.?
-
Three U.S. President died of hypertension. Theodore Roosevelt,Woodrow Wilson and Franklin Roosevelt, all died fromComplication from FLUCTUATION OF HYPERTENSION
| Latanoprost 0.005% (XALATAN) | PHARMACIA |
| Travoprost 0.004% (TRAVATAN) | ALCON |
| Bimatoprost 0.03% (LUMIGAN) | ALLERGAN |
| Unoprostone 0.15% (RESCULA) | NOVARTIS |
ANY FLUCTUATION IS BAD

HIGHER RISK OF PROGRESSION NTG
COMMON IN NTG
NTG PATIENT'S VF AND FUNDUS
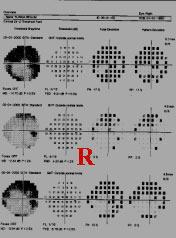

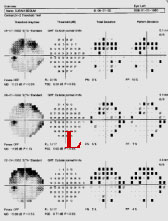
AN ESTABLISHED CASEOF NTG.HER IOP IS NOW10mmHg B/E
LAST PT'S 24 MONITORING OF BP

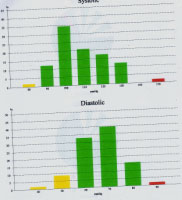
24 hrs. Monitoring of a LTG pt. done with mild hypertension. She is on Atenolol 50mg in the morning Amlodipine 5mg at bed time. After shehas been diagnosed as NTG on Jan 02 and on Azopt thrice daily. During Night her diastole drops below 60.She has been advised to consult her cardiologist about her low diastole tendency at late Night.
COLOR DOPPLER SONOGRAPHY
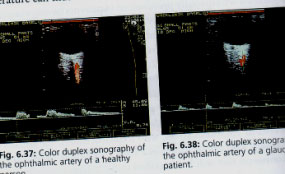
HEALTHY............ .......GLAUCOMA PATIENT
Color doppler, sonography,is used on Glaucoma patients to determine the blood velocity in several vessels leading to the eye. This enables a calculation of resistance index, a parameter for downstream resistance to flow that is of particular Importance in glaucoma. Here an ophthalmic artery of a healthy individual and the same test on Glaucoma pt.with reduced perfusion is shown.
OVER VIEW

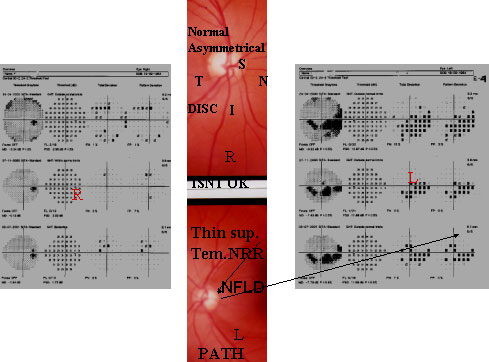
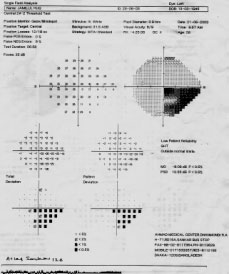
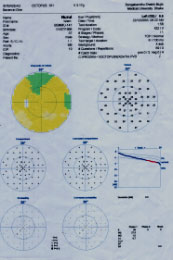
This middle aged man complains of frequent Change of his reading glass. IOP normal. B/E.V.A 6/6 B/E. With +78 deep cupping has been noticed. B/E.ISNT rule is not ok. Rt. sup NRRis thinner than nasal NRR. In Rt. Fundus both Sup & inf. NFLD are seen which well correlates with the VFD Sup & inf arcuate SCOTOMAS.So, the second Rt. field is reliable and taken as baseline VF and an early case of NTG.
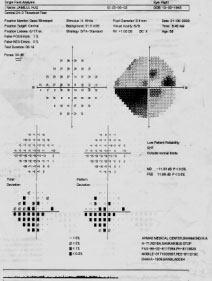
Lt. Fundus shows inf. temp. NFLD as well as inf.notching, which well correlates with VF's Supra Nasal arcuate SCOTOMA joins the upper nasal step. Lt. temp. pallor of the disc well correlates with the Upper Nasal step.
SO BOTH THE SECOND FIELDS ARERELIABLE & TAKEN AS A BASE LINE FIELD AND WELL CORRELATES WITH THE FUNDUS, A CASE OF EARLY NTG.

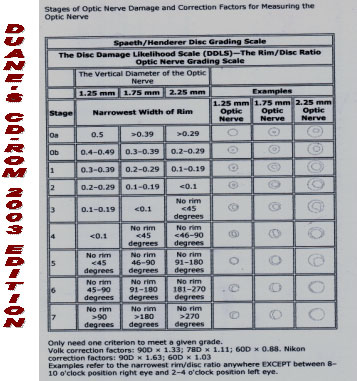
DUANE'S CD-ROM 2003 EDITION
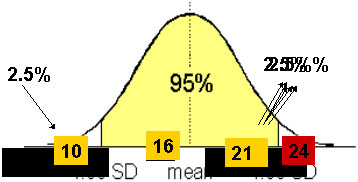
THE IOP IS DISTRIBUTED IN THE NORMAL POPULATION IN A GAUSSIAN OR "BELL-SHAPED" MANNER
WHY 21 CONSIDERED "NORMAL"
TARGET PRESSURE RANGES; Goal for lowering IOP
|
Intraocular Pressure
|
||
Damage Pressure(mmHg) |
Decrease Desired(%) |
Absolute level desired (mmHg) |
Above 35 |
About 50% |
18-25 |
25-35 |
About 40-50% |
13-18 |
21-25 |
About 40% |
14-15 |
17-20 |
About 40%-30% |
12-15 |
13-15 |
About 20% |
10-12 |
10-12 |
About 10%-20% |
8-9 |
A target pressure will not damage the optic nerve any further.
TARGET IOP



IOP, Slight disc damage
IOP, moderate disc damage
IOP, Serious disc damage
17-18mmHg
15 mmHg
12 mmHg
Slight damaged mean a change in the optic nerve ± small VFD
Dr. Rick Wilson
Establishing Initial Target IOP (CIGTS Study)
Target IOP = (1 - Reference IOP + Visual Field Score ) x Reference IOP 100
Example
MODE OF ACTION
|
IOP Decrease |
Decreases Aqueous Production |
Increases Uveoscleral Outflow |
Increases Trabecular Outflow |
|
|
Brimonidine |
20%-30% |
 |
 |
. |
|
ß-Blockers |
20%-30% |
 |
. |
. |
|
Pilocarpine |
10%-20% |
. |
. |
 |
|
Dorzolamide |
15%-20% |
 |
. |
. |
|
Prostaglandin |
25%-30% |
. |
 |
. |
DISEASE CAPSULE ; POAG
1. EPIDEMIOLOGY
2. MINOR RISK FACTORS
3. SYMPTOMS
4.SIGNS
Angle & Trabecular Meshwork |
Normal |
Lens |
Normal |
Intra ocular pressure |
Elevated |
OPTIC NERVE |
Cupped |
TREATMENT
TILTED DISC/HIGH MYOPIA
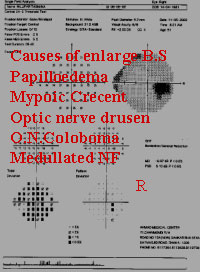

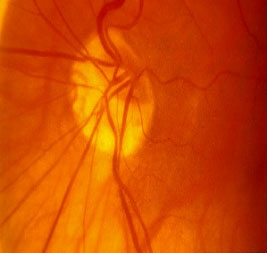
 Disc size is due to PPA. When it isseen more likely to be Cong. A tipFrom SPAETH. Pale disc is due toPseudophakic. Thin NRR does notMatch with the VF.
Disc size is due to PPA. When it isseen more likely to be Cong. A tipFrom SPAETH. Pale disc is due toPseudophakic. Thin NRR does notMatch with the VF.
TILTED DISC 1
TILTED DISC 2
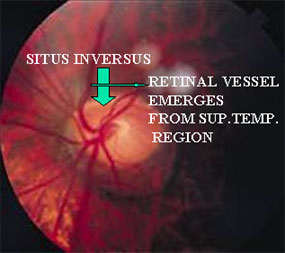
TILTED DISC 3
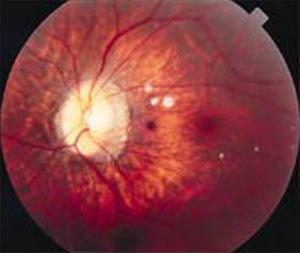
TILTED DISC 4
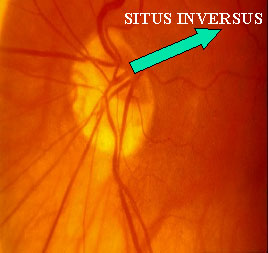
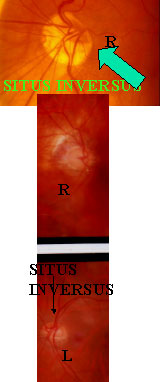
RETINAL VESSELS EMERGE FROM THE DISC TISSUE SUP.TEMP. RATHER THAN NASALLY (SITUS INVERSUS)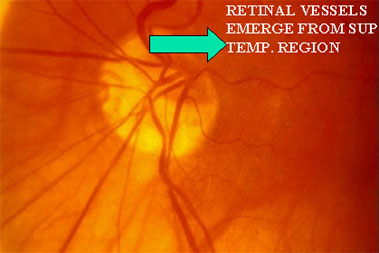
NOW ANSWER OF THE TD-1
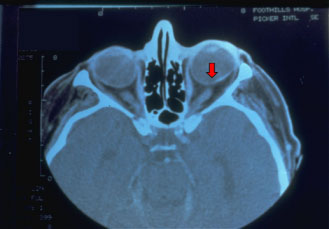
CT Scan of Tilted Disc
Tilted disc with retinal ectasia
TILTED DISC HAS
- TILTED DISC SYNDROME OCCURS TO1%-2% OF THE WHOLE POPULATION
- THE LONG AXIS OF THE OVAL DISC ISOBLIQUELY DIRECTED,UPPER & TEMPORALREGIONS OF THE DISC ARE ANTERIORTO THE INFERONASAL AREA.
- THE RETINAL VESSELS EMERGE FROM THE DISC IN THE SUP.TEMP AREA, RATHERTHAN NASALLY(SITUS INVERSUS)
- HYPOPIGMENTATION INEFRONASALLYTO DISC
- IN CONTRAST WITH THE GLAUCOMATOUSDISC,TEMPORAL DISC USUALLY IS NOT EXCAVATED BUT IS EVEVATED SUPERIORLY
- AN OBLIQUE DIRECTION OF RETINALVESSEL
- A CRESCENT ON THE SIDE OF THE DISCDEPRESSION
- HIGH MYOPIA OR MODERATE OBLIQUEMYOPIC ASTIGMATISM PRESENT
- OBLIQE INSERTION OF THE OPTIC NERVE IN THE GLOBE
- IN TITLES DISC RETINAL ECTASIA WILL BE FOUND IN CT SCAN
ISNT NOT OK BUT NORMAL VF

CASE REF. BY DR.SABBIRISLAMIA
NO NFLD& HEALTHY NRR
NOT STICKING TO ISNT RULE
THUMB NAIL OF FUNDUS
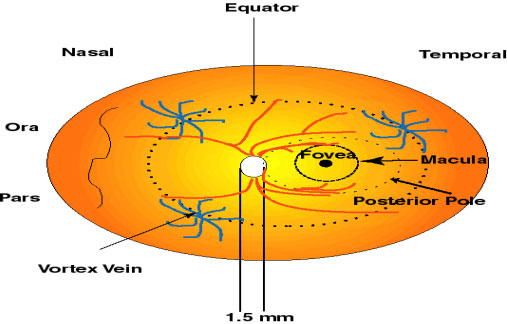
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF DISC
HORIZONTAL C:D 0.4, CUP OCCUPIES 4/10 WIDTH OF DISC
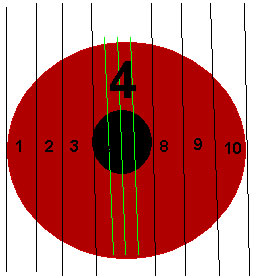
Measuring Disc Diameter
-
Normal optic nerve's head size is 1.5mm in diameter.
-
But the disc diameter vary from 0.96mm to 2.91mm
-
As a result, physiological cup can be as small as 0.1:1 or as large as 0.8:1.
-
Clinical estimation of optic nerve can be done by WELSCH ALEENOR
-
Slit lamp with +78D or +90D
By WELSCH ALEEN Ophthalmoscope
The smallest white round spot of the Welsch Aleen ophthalmoscope casts alight of 1.5mm in diameter on the retina.This retinal spot size remains constant in phakic eyes with refractive errorsbetween -5.00 & +4 dioptres. When this size coincides with the disc, thenthe disc diameter will be 1.5 mm.In eyes with large physiological cups due to large discs the area illuminated isless than the area occupied by the cup.
BY SLIT LAMP
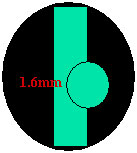
BAYER is the lead author andhe is the first publication of the scale
Conversion Chart
Manufacturer |
. |
LENS |
. |
. |
60D |
78D |
90D |
VOLK |
0.88 |
1.11 |
1.33 |
NIKON |
1.03 |
. |
1.63 |
Measuring Disc Diameter
- Manufacturer specific
Example;
1.6mm(Vertical length)x1.11(Volk 78)=1.78mm, will be the disc diameter.
SIMPLE DRAWING
NORMAL & GLAUCOMATOUS OA
ASYMMETRIC DISC
Optic Nerve head change in Glaucoma
NOTCHING
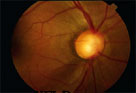
NFLD
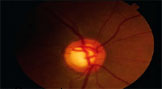
BEANPOT
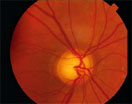
Circumlinear
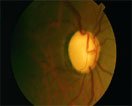
No RIM at all

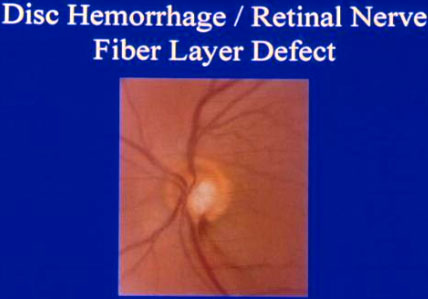
Disc hemorrhage
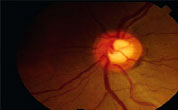
Beanpot
ONH GLAUCOMA
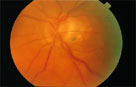
Vertical elogation with PPA
Baring of Circumlinear Vessel



Dr.Jeff Henderer
Murshed. Good case. I'm here at the Academy meeting in Orlando. Greetings from Disney World! I think this guy looks normal. The nerve OD looks a bit odd with the superior rim thickness, but I'm thinking that's a normal variant. I don't see the NFL defect. I'm not bothered by the vasculature in this monoscopic view. The PPA I never pay much attention to, but if it gets larger (the beta zone) then that can be glaucoma. I'd watch him. Great video by the way! I'm seriously impressed! Good to hear from you and I hope you are well too. Take care!
Jeff
Baring of Circumlinear Vessel
This vessel was originally at the rim but is now hanging out in space. A sign of GLAUCOMA and indication of Progressive cupping.
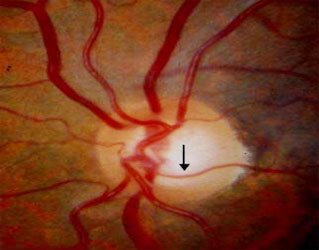
OPTIC NERVE HEAD CUPPING IS A UNIFYING FEATURE OF ALL GLAUCUMAS

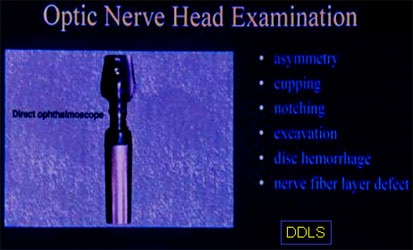
DISC EXAMINATION BY AN EXPERIENCED GLAUCOMA SPECIALIST WAS ACCEPTED AS GOLD STANDARD.
Evaluation of OPTIC NERVE HEAD & NFLD
| QUALITATIVE | QUANTITATIVE |
|
|
OLD IS GOLD

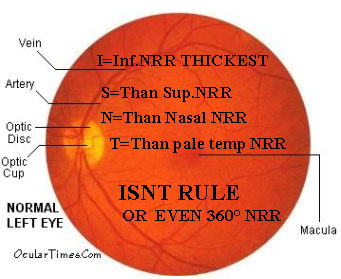
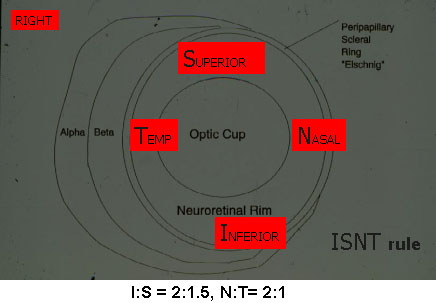
NRR
NORMAL NERVE-NRR SHAPE
Theories of Glaucoma damage not yet
Established Two broad categories:

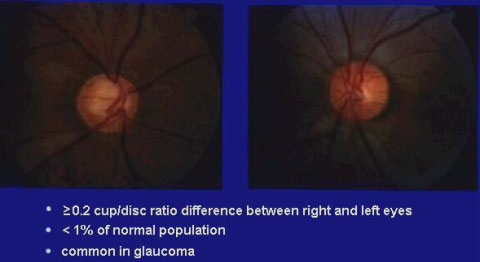
Asymmetric DISC
Tissue between The cup & disc is NRR made of nerve & capillaries So, looks red to orange
DIFFUSE & LOCALIZED FIELD DAMAGE
PATHOGENITIC CONCEPT
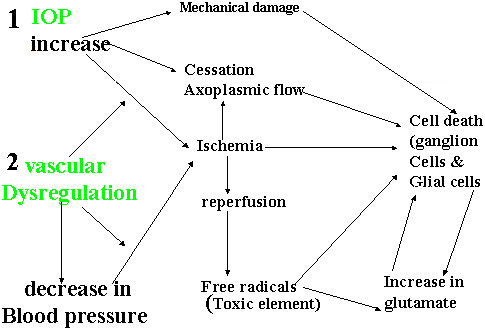
IOP and Glaucoma
Normal "IOP" is debatable value between 18-24 More 60%> population have IOP below 21 mmHg
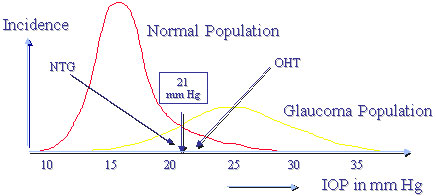
IOP curves of the Normal- and Glaucoma Population
WHY CENTRAL 30/24 DEGREE
WHY 24 ° -2
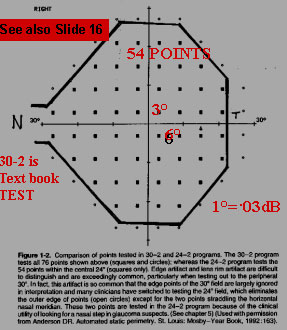

If we keep 30 ° nasal field & the rest peripheral points are discarded(22) taking 76 points in 30-2 instead of taking 24-2 where 54 points are taken which makes the patient less fatigue and test is reliable too, by discarding the peripheral points of no significant change in the field seen. So, now all the leading clinics are using 24-2.Left picture is from the "BUDENZ" atlas which also Says this.
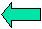
THE VISUAL FIELD
The visual field is the extent of the area which one fixating eye can see.
Periphery is five times the central 30 °area. A static perimetry examination would take almost one hour to do the whole field. For the periphery, Goldman Kinetic perimetry is more accurate and faster. Kinetic type of perimetry can also be done in the HUMPHREY
Manual Goldmann Perimetry
The original Goldmann perimeter remains a valuable instrument.
IN 1945 FIRST CUPOLAPERIMETRY WAS DESIGNEDBY PROFESSORHANS GOLDMANBERN, SWITZERLAND.
FRUCTUATIONS
Compare short and long term fructuation with the movements of the waves and tides.
The sensitivity of the eye varies from moment to moment & from day today, as do alertness of the patient &the critera the Pt.uses in answering.

SUSPECTED

EARLY NASAL STEP
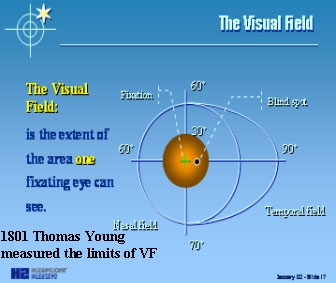
Early inf. NASAL step is seenhere, if it is repeatable in thenext VF it will be a case of earlyPOAG.
GLAUCOMATOUS DEFECT
- Paracentral scotoma(BA) 77%
- Nasal step 30 ° 14%
- Nasal Step in periphery 7%
- Temporal Wedge 3%According to Drance & Armaly
In early stage with fundus photo, diagnosis of GLAUCOMAis very difficult to comment
STEROID
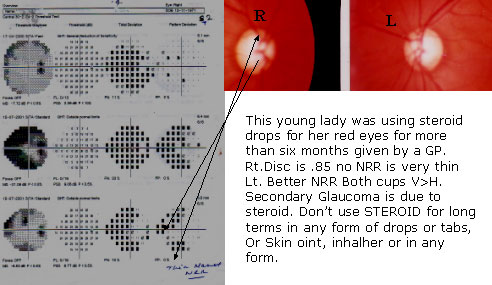
Field is well correlated with the DISC
Children of Glaucomatous pt. should use steroid with caution
Risk factors for Steroid Induced GLAUCOMA
MECHANISM FOR IOP ELEVATION
CORTICOSTEROIDS CAUSE ELEVATION OF IOPBY DECREASING THE FACILITY OFAQUEOUS OUTFLOW.
According to BECKER & ARMALY 5%-6% of normal populationresponder to steroid given over a 4-6 weeks period.
MOST POTENT |
S |
LESS POTENT |
|
|
|
COMPARE
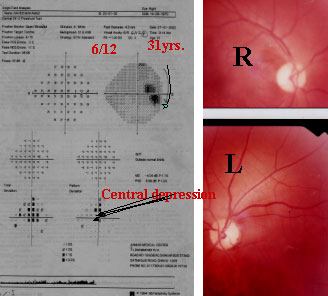
Rt, picture shows very thin Sup &Inf NRR which corresponds the Sup& Inf. acurate scotomas in the PSD plot chart.An established case of POAG. Middle aged woman of 55yrs.
CORRELATION WITH OPTIC DISC
PALE DISC
This young man of 31yrs.Came for unexplained low V.A Does not improve With P.H above 6/12H/O severe headache& vomiting too. C.T Scan normal. C'D,B/E 0.5 DISC PALECENTRAL Scotomas Seeing both the fields In PSD plot chart, Both rim & Disc are Pale without cupping=Neuro case. Think of Nutritional optic.
Neuropathy, Methanol ON, or Domin any optic Neuropathy. A NEURO Case. See for Color Vision, Vit B 12 & Folate Levels?
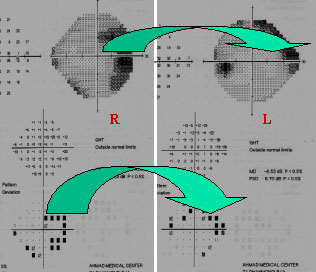

Slight asymmetry of the disc. Pallor disc is R>L. Pallor disc is not Seen in glaucoma Unless late stage. V.A6/6 B/E & IOP normal Lady of 25yrs.She hasA right incongruous Hemianopia, think of NEUROLOGICAL case. Tough case SCAN can give the result. M/O One child, she had H/O severe PPH think of Stroke, or severe haem,May cause occipital Ischemia?
Neuro 1

This young man of 32yrs Total color blind R/E 6/9 with -1,-2.5180.L/E C.F 5 feet.Disc and IOP are Normal. FT R/E 32,L/E 0dB. Diagnosis To be confirmed byCT/MRI. BITEMP HEMIANOPIA Lesion situated at the Chiasma, by Interrupting the Crossing nasal fiber,Bring about a loss in The temporal portion Of the field of each eye.
Lesion depends on the growth of the tumour may be Congruous or Incongruous.
Neuro 2
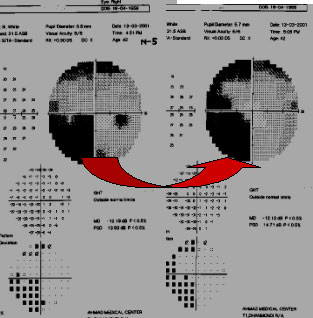
"Pie in the Floor" this Young is middle aged Very and restless (Motor Impersistence) H/O mild Hemi paresis on the left Side for 6 months. MRI On 03.03.01 "Late Sub Acute Infarcts at rt. frontal & Parietal regions. Field done on 13.03.01 Shows Left homonymous Quadrantanopia (Pie in Floor )due to lesion in the superior fibers of the rt.optic radiation signs of Rt.Parietal lobe function.
Neuro 3
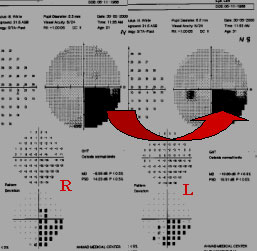
This young Doctor had H/O Convulsion.V.A,6/24 B/E does not improve with P.H.& also does not correspond with theFT 36 dB,35dB. He has also
- Finger agnosia
- Rt./Lt. Confusion
- Agraphia
- Does not respond to command
- Dyscalculia
OPTIC RAD.TEMP.L.LESION FIELD DEFECT "PIE IN THE SKY" PARIETAL LOBE FIELD DEFECT "PIE ON THE FLOOR"
Neuro 4

This 50yrs. old man known as DM &BP. H/O had Lt. sided Hemi paresis. Lt. upper Incongruous quadran tic hemianopia "Pie in the sky"Should be Confirmed by MRI or MRA.
Neuro 5

A known diabetic noticed sudden loss of Upper lt. field. Her vision is 6/6 L/E when She looks downward. R/E V.A.6/6.Sup or inf ALTITUDINAL VFD results from damage to the upper or lower pole Of the disc.
ALTITUDINAL FD
ALTITUDINAL FIELD DEFECT
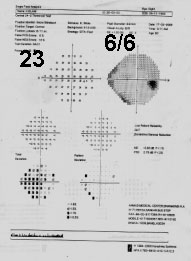
24-2 SF B/E

POOR FOVEAL THRESHOLD

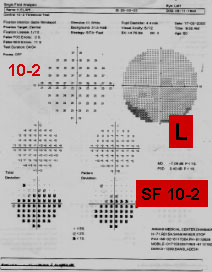
WHEN POOR FOVEAL THRESHOLD MACULAR 10-2 ISMANDATORY
UPPER TEMPORAL BRANCH VEIN OCCLUSSION
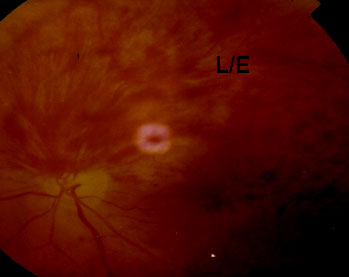
ALTITUDINAL FIELD DEFECTS MAY BE UNILATERAL OR BILATERAL CAUSESE ARE
RETINAL CAUSES
OPTIC NERVE LESION
LESION IN CEREBRAL CORTEX
Neuro 6
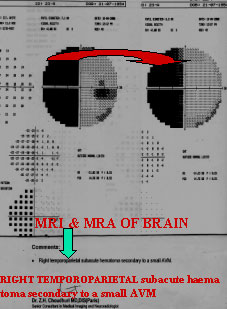
PERIMETRY IS,HOWEVER,MANDATORY WHEN INDICTED BY THE CLINICAL HISTROY,THE EYE EXAM, OR BRAIN, ORMRA/MRI OR CT FINDINGS.
CHIASMAL COMPRESSION
High Myopic cylinder. First reported to an ophthalmologist.His main complain was loss of bilateral temporal vision.
BINASAL HEMIANOPIA
Brief History
WHAT'S YOUR DIAGNOSIS
First ruled out common cause of Binasal inf.nasal quadrantonopia
RARE CAUSE
Here for final diagnostic investigation depends on available resource to diagnose Internal Carotid artery aneurysm we advice for MRA & MRI (NORMAL STUDY)
JEFF HENDERER REPLIES
Murshed,
Great to hear from you again! I look forward to seeing you in California! I have never seen a case like this, but I think that you are correct in everything you are doing and thinking. In fact I was thinking the aneurysm as I read through your workup and then when you said it "bingo" I thought! Well, its a rare condition and a very rare field, but the consequences of missing this diagnosis are so great that I think it is an appropriate use of resources. Rupture would almost certainly be horrible, if not fatal. By the way, I agree with you on the reliability of the fields. Take care!
Jeff
BINASAL
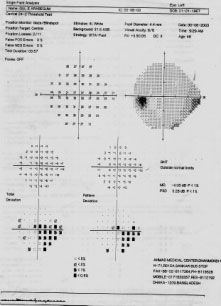
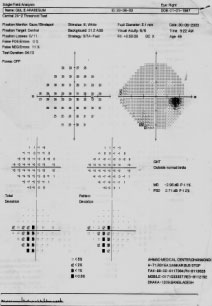
A lady came for field for uncomfortable in near reading.C:D .3 R/E,.5 L/E 6/6 O.U N 5 B/E IOP WNL Disc normal
NEUROLOGICAL FIELD DEFECT
| OPTIC NERVE | IPSILATERAL BLINDNESS |
| OPTIC CHIASM | BINASAL HEMIANOPIABITEMPORAL HEMIANOPIA |
| OPTIC TRACT | CONTRALATERAL HOMONYMOUSHEMIANOPIA |
| LATERAL GB | SAME AS ABOVE |
| GENICULO CALCARINETRACT (VISUAL RADIATION) 1)UPPER DIVISION 2)LOWER DIVISION |
1) CONTROLATERAL LOWER HOMO PARI.LOBE.LESION QUADRANTANOPIA (PIE IN THE FLOOR) 2) CONTR UPPER HOMO QUADRAN TEMP.LOBE.LESION (PIE IN THE SKY) |
| VISUAL CORTEX | CONTROLATERAL HEMIANOPIA WITH MACULAR SPARING |
FD OCCIPITAL RADIATION OR THE STRIATE CORTEX
TO DETECT TEPORO OCCIPITAL FD NEEDS
BITEMPORAL HEMIANOPIA
EASTABLISHED POAG
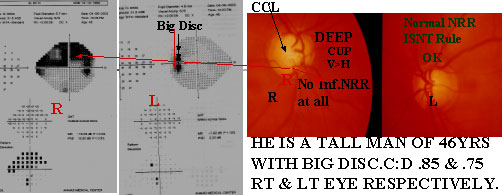
Right disc has no inferior NRR at all as well as nasal shifting of the vessels are seen with deep cupping and lamellar dot signs are seen which well corresponds with the right field. Dense arcuate scotomas emanating from the blind spot to join the superior arcuate scotoma later joins the upper nasal step to form half dense arcute ring scotoma. His IOP was 24mmHg R/E when first diagnosed. Now he is on anti Glaucoma drops B/E and IOP 14mmHg.Left field & fundus are normal.Lt.fundus shows inf.temp. PPA in an emmatrop is suspicious.
DENSE SUP ARCUATE SCOTOMA
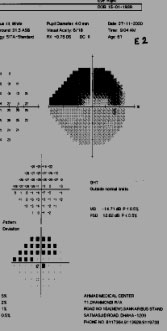
DENSE SUP ARCUATE SCOTOMASEMANTING FROM THE BLIND SPOTJOINS THE SUP ARCUATE SCOTOMALATER JIONS THE NASAL SUP NASALSTEP. FIELD MATCHES WITH THIN INFNRR.A CASE OF ESTABLISHED POAG.
DISC SHOWS NO INFERIORNEURO RETINAL RIM
D/D OF ARCUATE SCOTOMA
- CHORIORETNIAL LESIONSJUXTAPAPILLARY CHOROIDITIS &RETINOCHORODITIS MYOPIA WITH PPA
- OPTIC HEAD LESIONDRUSEN, PAPILLITIS, COLOBOMAS,CHRONIC PAPILLOEDMA
- ANTERIOR OPTIC NERVE LESIONRETROBULBAR NEURITIS,ELECTRIC SHOCK
- POSTERIOR LESION TO VISUAL PATHWAYPITUTIARY ADENOMA,PSEUDOTUMOUR CERIBRI
ADVANCE POAG




This middle aged woman diagnosed POAG 5yrs.back.V.A R/E 6/9Tubular.L/E 6/6.C;D R/E .99/1,L/E .5.Rt. VF shows only a small central field withan island of small temporal field. Lt.shows cluster of scotomas in the mostSuspected & expected zone Sup & infra nasal quadrant.L/E an early POAG.Rt. Eye an advanced POAG. She was very irregular in putting drops.


This school teacher of 45yrs.enjoys 6/4.5R/E& 6/6L/E.Binoculr Esterman shows 4 adjacent scotoms in the Sup. Field, & 6 scotomas seen in the lower
Temp. zone. Here out of 120 points, he can see 109 & cannot See 11 points. When not seen crosses 10>in screening test than full Threshold test to be done. This is an advance case of POAG R>L.
BRIEF HISTROY
PHASING


SCOTOMAS
40% OF PATIENTS. OTHEREARLY MANIFESTATIONS OF GLAUCOMA
NEIL T.CHOPLIN RUSSEL P.EDWARDS ............................................................................Page 119 2ed.
NTG


First detected when he comes for near reading glass.NTG Fixation threatening, localised VFD,
30% of all POAG,30% IOP to be reduced
JPOAG

Came to an eye specialist, as he can not see the black board.
THE SNEAK THIEF OF SIGHT

OPTIC NERVE

This young man with color Blind. L/E V.A.6/24 No P.H Improvement. R/E 6/6. Poor FT L/E 24dB CECOCENTRAL SCOTOMA PAPILLOMACULAR BUNDLE CONNECTING WITH THE FIXATION TO BLIND SPOT CAUSES ARE1.DOMINANT OPTIC ATROPHY2. LEBER'S O.A.3.OPTIC NEURITIS4.TOXIC/NUTRITIONAL OPTIC NEUROPATHY
''IT JUST GOT IN MY WAY''
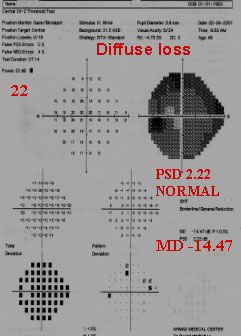
POOR FT 22dB & VERY DEPRESSED GRAY
SCALE WITH MD -14.4 ,BUT PSD ;value normal
2.22INDICATES A CATARACTOUS VFD.PT'S
V.A WAS6/24. It's a normal field Study.
High MD is due to CATARACT
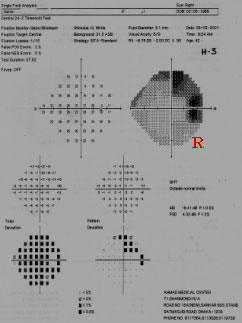
CRITERA OF HIGH MYOPIA
This 42yrs. Woman is a high Myop. R/E 6/9 with - 12,--2 90 ° L/E 6/6 with --5.5,Her both Fields are normal inspite of Supra temporal arcate scotomas.
Criteria of High Myopia
GLAUCOMA AT A GLANCE
and treatment can save your sight. Testing for Glaucoma is simple, quick and painless.
they have it. Of them 7 million are totally blind. Highest number of blind due to Glaucoma are
in NIGERIA. Half of this patient are from ASIA.
blind didn't have to be. Then what about BANGLADESH.
PLEASE THINK!!!
PREVENTION IS BETTER THAN CURE
EARLY DETECTION
Early Detection of Glaucoma
There are several methods claiming to detect glaucomatous damage in the very early stage.
Such As:
REFERRED
OPINION . IT IS VERY TOUGH TO DIAGNOSE AN EARLY POAG GLAUCOMA.BECAUSE OF
INDIVIDUAL & INTEROBSERVER SUSPECTED DISC EVALUATION
POAG
REFERENCE WILL RELIEF
GLAUCOMA AWARENESS
treatable if caught in its early stage.
SO YOU'RE A GLAUCOMA SUSPECT, NOW WHAT ?
ARE YOU A PARENT WITH GLAUCOMA ?
OF "NURUL ISLAM CLINIC" OR DR.MD.FAZLUL HAQUE(SUBECHA PLAZA) FOR NON
CONTACT PUFF TONOMETRY"
HOW DOES ONE COPE WITH GLAUCOMA
WHAT CAN YOU DO TO RAISE GLAUCOMA AWARENESS ?
AT RISK
ADVICE
BE RECORDED WHEN YOU SEE FLUCTUATION OF B.P.CONSULT YOUR CARDIOLOGIST ABOUT
B.P/IOP
IN DIVIDED AMOUNT THROUGHOUT THE DAY
HUMPHREY vs OCTOPUS
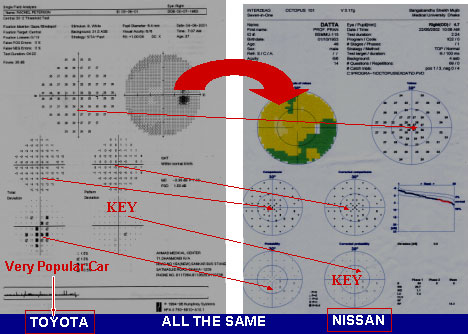
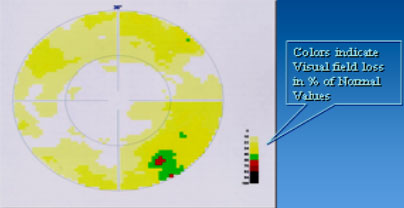
COLOUR INDICES
Comparison Gray Scale
PERIMETER PARAMETER & SCALE
Parameter |
Humphrey 1994-1998 |
Octopus 101 1993 |
Bowl type |
33 cm a-spherical |
42.5 cm spherical |
Back ground |
31.5 asb |
4asb/ 31.4asb |
Stimulus size |
Goldman 1to V |
Goldman 1 to V |
Stimulus present |
200ms |
100ms/200ms |
Dynamic range |
0-50 Db |
0-40 dB |
MD/MD |
Mean deviation |
Mean defect |
PSD/LV |
Pattern stan. devia |
Loss variance |
CPSD/CLV |
CPSD |
CLV |
SITA/TOP |
SITA,SF 3-5min,SS 4-8 |
TOP 2-3 min |
Reliability RF |
FL20%,FP10%,FN15% |
RF 15%-20% |
Tracking gaze |
YES |
NO |
GHT |
YES |
NO |
BEBIE CURVE |
NO |
YES |
Parameters
Humphrey |
Octopus |
|
Space |
Small Compact |
Big Space/Not 300 |
Neck to Neck |
Zeiss/Humphrey |
Haag-streit |
Price |
We can reduce price by using mouse from local market,150Tk/,instead of brand key board. HP B/W printer (15,000tk) local motorize table. We canSave upto 4 lac taka |
Key Issue
Understand the Principles
HUMPHREY IS GOLD STANDARD
NO MACHINE IS BAD,IT IS THE MAN BEHIND THE MACHINE
Gentle Request
Total deviation |
Octopus |
|
|
|
|
MD |
B/Y |
|
|

|
|
PROVIEW TONOMETER
THANK YOU ALL
Dedicated to the memory of my father
Prof. Dr. Nawab Ali Ahmed M.B.(Cal) FRCS
AHMAD MEDICAL CENTER
Dhaka, Bangladesh